Li Lily Wang Laboratory
-
Li Lily Wang Laboratory
- Principal Investigator
- Research
- Our Team
- Publications
- Careers
- Research News
Research
The current research interest of our laboratory is to define the mechanisms by which immune checkpoint proteins regulate anti-tumor immune responses and to develop rational therapeutics for cancer immunotherapy. Specifically, we focus on delineating the mechanisms by which a novel immune checkpoint protein, V-domain Immunoglobulin Suppression of T cell Activation (VISTA), modulates immune responses to tumors. Our research group has published a series of original research and review articles that address the inhibitory roles of VISTA during the development of anti-tumor immunity, autoimmunity, and inflammatory diseases. We have shown that VISTA is a critical immune checkpoint protein that controls myeloid cell- and T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity, therefore is a valuable target for cancer immunotherapy. Currently, we are committed to discovering novel inhibitory receptors that interact with VISTA and developing effective approaches that block VISTA-mediated immune checkpoint pathway and improve the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.
Biography
Dr. Li Lily Wang (PhD) is currently a Full Staff in the Department of Translational Hematology and Oncology Research, Taussig Cancer Institute, Cleveland Clinic. She is an Associate Professor in the Department of Molecular Medicine at Case Western Reserve University (CWRU), Cleveland, OH. Dr. Wang is leading a group of scientists and trainees to study fundamental mechanisms of antitumor immune responses. Research projects involve investigating the signaling mechanisms and functions of novel T cell co-inhibitory receptors and developing novel therapeutics targeting immune checkpoint proteins for cancer treatment. Dr. Wang is one of the original inventors that identified VISTA as an important immune checkpoint protein and a promising target for cancer immunotherapy. Dr. Wang’s research group have published extensively regarding the novel mechanisms by which VISTA modulate antitumor immunity. Her team recently has made another breakthrough discovery that LRIG1, a signaling inhibitory receptor, functions as a novel VISTA-binding receptor and a next generation immune checkpoint receptor target for cancer immunotherapy. These studies have provided key insights that will guide efforts for developing novel cancer immuno-therapeutics targeting this important immune checkpoint pathway. As such, Dr. Wang’s research has generated high impact in the field of Tumor Immunology and Cancer Immunotherapy.
Education & Professional Highlights
"CIMER Trained Mentor" indicates the principal investigator has completed mentorship training based on curriculum from the Center for the Improvement of Mentored Experiences in Research, aimed at advancing mentoring relationships and promoting cultural change in research.
More updates coming soon.
Research
The current research interest of our laboratory is to define the mechanisms by which immune checkpoint proteins regulate anti-tumor immune responses and to develop rational therapeutics for cancer immunotherapy.
Specifically, we focus on delineating the mechanisms by which a novel immune checkpoint protein, V-domain Immunoglobulin Suppression of T cell Activation (VISTA), modulates immune responses to tumors. Our research group has published a series of original research and review articles that address the inhibitory roles of VISTA during the development of anti-tumor immunity, autoimmunity, and inflammatory diseases. We have shown that VISTA is a critical immune checkpoint protein that controls myeloid cell- and T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity, therefore is a valuable target for cancer immunotherapy.
Currently, we are committed to discovering novel inhibitory receptors that interact with VISTA and developing effective approaches that block VISTA-mediated immune checkpoint pathway and improve the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy.
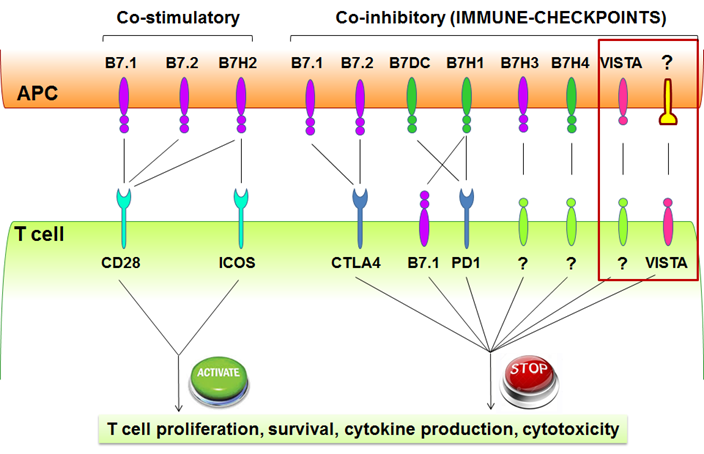
Figure 1. The B7 family co-signaling molecules regulate T cell responses. Co-inhibitory molecules, such as CTLA-4, PD-1, and VISTA are also called “immune-checkpoint proteins”. They play a critical role in maintaining T cell peripheral tolerance and controlling autoimmunity.
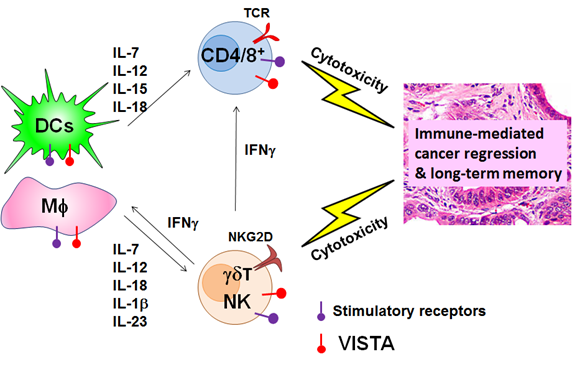
Figure 2. V-domain Immunoglobulin Suppression of T cell Activation (VISTA) is a novel immune-checkpoint protein that regulates both innate and adaptive immunity against cancer.
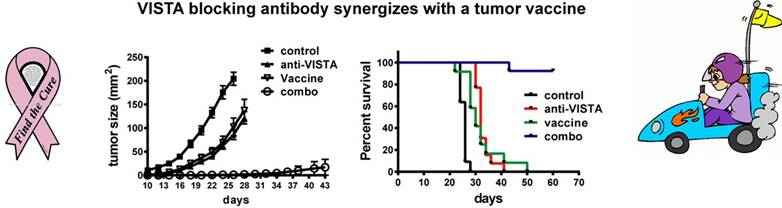
Figure 3. A VISTA-blocking monoclonal antibody synergizes with a cancer vaccine to eradicate tumor cells and improve host survival.
Our Team
Selected Publications
1. Le Mercier I, Chen W, Lines JL, Day M, Li J, Sergent P, Noelle RJ, Wang L (2014) VISTA regulates the development of protective anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Research, 74:1933-1944. PMC4116689
2. Xu W, Tạ MH, Malarkannan S, Wang L (2018) Review: The structure, expression, and function of immune-checkpoint protein VISTA as a critical regulator of anti-tumor immunity, autoimmunity, and inflammation. Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 2018 May 15(5):438-446 PMC6068175
3. Xu W, Dong J, Zheng Y, Zhou J, Yuan Y, Ta H, Miller H, Olson M, Rajasekaran K, Ernstoff M, Wang D, Malarkannan S, Wang L (2019) Immune checkpoint protein VISTA regulates antitumor immunity by controlling myeloid cell-mediated inflammation and immunosuppression. Cancer Immunology Research PubMed PMID:31340983; NIHMSID:NIHMS1535762
4. Zhang K, Zakeri A, Alban T, Dong J, Ta HM, Zalavadia AH, Branicky A, Zhao H, Juric I, Husich H, Parthasarathy PB, Rupani A, Drazba JA, Chakraborty AA, Ching-Cheng Huang S, Chan T, Avril S, Wang LL. VISTA promotes the metabolism and differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells by STAT3 and polyamine-dependent mechanisms. Cell Reports 2024 Jan 3;43(1):113661. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113661. PMID: 38175754.
5. Hieu Minh Ta, Dia Roy, Keman Zhang, Tyler Alban, Ivan Juric, Juan Dong, Sachin Patnaik, Cassandra Gilmour, Amin Zakeri, Prerana B Parthasarathy, Amit Rupani, Yee Peng Phoon, Brian Gastman, Timothy Chan, Li Lily Wang. LRIG1 engages ligand VISTA and impairs tumor-specific CD8+ T cell responses. Science Immunology, 2024 May 17;9(95) PMID: 38758807 DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adi7418
Careers
Training at Lerner Research Institute
Our education and training programs offer hands-on experience at one of the nationʼs top hospitals. Travel, publish in high impact journals and collaborate with investigators to solve real-world biomedical research questions.
Learn MoreResearch News

The protein VISTA combines with a newly discovered inhibitory receptor LRIG1 to directly block our T cells from working during immunotherapy.

The discovery, made by a collaborative group of Cleveland Clinic researchers, opens the door to new avenues of research and reveals promising drug targets.

Drs. Mian, Gupta and Hwang—a multi-disciplinary team of researchers and clinicians—will look for ways to optimize immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy, including testing novel combinatory treatments and identifying predictive biomarkers of treatment response
