Stanley Hazen Laboratory
-
Stanley Hazen Laboratory
- Principal Investigator
- Research
- Our Team
- Publications
- Careers
- Research News
Research
A long term goal of my laboratory is to understand the ways in which our immune system contributes to diseases like heart disease and asthma. I have several major areas of focus. One centers on the role of myeloperoxidase, a protein found in white blood cells that plays an important role in fighting infections, but which we have discovered also participates in development of heart diseases. A second area focuses on the role of microbes in our intestines (called gut flora) in heart disease. Another area focuses on the HDL particle (carrier of good cholesterol in the blood).
Biography
Stanley Hazen, MD, PhD, received clinical training in Internal Medicine and subspecialty training in Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism from Barnes/Jewish Hospital, St. Louis, MO, and a PhD in Biophysical Chemistry and Molecular Biology from Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO. He holds multiple leadership positions at the Cleveland Clinic including chair, Department of Cardiovascular & Metabolic Sciences, Lerner Research Institute, co-Section head, Preventive Cardiology & Rehabilitation, Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute, and Director, Center for Microbiome & Human Health. Dr. Hazen sees patients within the Preventive Cardiology Clinic, specializing in preventive cardiovascular medicine care of patients including treatment of hyperlipidemia, hypertension, obesity and diabetes. He also sees patients within the Cardiovascular Rehabilitation program. His research interests include studies of mechanisms for the development of cardiovascular disease, with emphasis on understanding the role of the gut microbiome, inflammation and oxidant stress in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and other inflammatory diseases.
A renowned physician scientist, Dr. Hazen has made pioneering discoveries in new understandings of mechanisms contributing to cardiovascular and inflammatory disease research. He is credited with numerous seminal discoveries linking gut microbial pathways to cardiovascular disease pathogenesis, as well as enumerating the role of myeloperoxidase and other inflammatory and oxidative pathways in cardiovascular disease. Dr. Hazen is among the top 0.1% cited researchers in the world with over 140,000 citations. He has published over 475 peer-reviewed articles in top tier basic and clinical journals alike in the fields of atherosclerosis, lipoprotein metabolism, gut microbiome, inflammation, vascular biology, and other topics related to preventive cardiovascular medicine. His research in multiple areas has impacted clinical practice, and lays the foundation for FDA- and EU-cleared diagnostic tests for cardiovascular disease risk assessment in use worldwide. He is listed as inventor on over 100 patents, and his research has helped to spawn pharmaceutical development of cardiovascular disease drugs in clinical trials.
Dr. Hazen has received numerous awards including being the Inaugural recipient of the Top 10 Clinical Discovery of the Year (2011) Award, Clinical Research Forum; the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association “top 10 advance in heart disease and stroke science” award (2013); and the American Heart Association Distinguished Scientist Award (2017). Dr Hazen has been honored with election of membership into honorary societies in both science and clinical arenas alike, including the American Society for Clinical Investigation (ASCI) and the American Association of Physicians (AAP). Dr. Hazen is an elected fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). Dr. Hazen also is an elected member of the National Academy of Medicine, USA.
Education & Professional Highlights
Education & Fellowships
Fellowship - Barnes-Jewish Hospital
Endocrinology
St. Louis, MO USA
1996
Residency - Barnes-Jewish Hospital
Internal Medicine
St. Louis, MO USA
1994
Medical Education - Washington University School of Medicine
St. Louis, MO USA
1992
Medical Education - Washington University
St. Louis, MO USA
1992
Undergraduate - Washington University
St. Louis, MO USA
1985
Professional Highlights
- Chair, Gordon Research Conference on Oxygen Radicals
- Jeffrey M Hoeg Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology Award for Basic Science and Clinical Research
- Election, Association of American Physicians (AAP)
- Election, Fellow of American Heart Association Scientific Council for Arteriosclerosis
- Election, American Society for Clinical Investigation
Awards & Honors
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute Research Fellowship for Physicians Award, 1995-1997
- AAP, ASCI, and AFMR Certificate of Achievement Award, 1997
- Marilyn Hansen American Thoracic Society Award, 1997
- Junior Faculty Award, American Federation of Medical Research, 1999
- Gill Heart Institute Physician Scientist Award, University of Kentucky, Lexington Ky., 2001
- Election, American Society for Clinical Investigation, 2003
- John J. Ferchill Award for Innovation, Cleveland Clinic, 2004
- Nomination, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator Award, 2004
- Vice-Chair, Gordon Research Conference on Oxygen Radicals, 2006
- Jeffrey M Hoeg Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular, 2007
Innovations & Patents
- Patent Title: Diagnostic Methods for Asthma; U.S. Serial Number 09/253,380
- Patent Title: Myeloperoxidase, a Risk Indicator for Cardiovascular Disease; U.S., Serial Number 10/039,753
- Patent Title: Treating Inflammation and Associated Complications; Patent Reference Number 09531-030P01 (Pending)
- Patent Title: Methods of Identifying Subjects at Increased Risk for Cardiovascular Disease; U.S. Serial Number 60/259,340 (Pending)
- Patent Title: Monitoring Anti-inflammatory and Anti-oxidant Actions of Therapies; U.S. Serial Number (Pending)
- Patent Title: Diagnostic Method for Identifying Subjects at Risk for Atherosclerosis and its Complications; U.S. Serial Number (Pending)
Memberships
- American Society for Clinical Investigation
- American Association for the Advancement of Science
- American Heart Association Scientific Council for Arteriosclerosis
- American Society for Investigative Pathology
- American College of Cardiology
Research
Overview
A long term goal of my laboratory is to understand mechanisms through which inflammation contributes to diseases like atherosclerosis and asthma. Several major research programs are currently under investigation. One research program focuses on the role of myeloperoxidase, a leukocyte heme protein, in promoting oxidant stress in vivo, and its participation in cardiovascular diseases. A second area focuses on HDL structure and function. A final area of research interest focuses on the role of intestinal microbiota in cardiometabolic disease.
All research projects rely heavily on chemical and analytical methods to identify specific reactions/products, their mechanisms of formation, and their use as probes to elaborate pathways responsible for disease. Research efforts in each program span from bench-to-bedside, including basic/genetic, cellular, animal model, and human clinical investigations.
Experimental Data
Experimental data and computational models for downloading
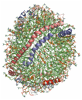
1) The refined structure of nascent HDL reveals a key functional domain for particle maturation and dysfunction
Wu, Z.; Wagner, M. A.; Zheng, L.; Parks, J. S.; Shy II, J. M.; Smith, J. D.; Gogonea, V.; Hazen, S. L. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14, 861-8 (2007).
Computational model:
 |
a) All-atom molecular model of the Solar Flares model of nascent HDL. Available at mi.caspur.it (accession code PM0074956). |
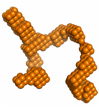
2) The double super helix model of high density lipoprotein
Wu, Z.; Gogonea, V.; Lee, X.; Wagner, M. A.; Li, X.-M.; Huang, Y.; Arundhati, U.; May, R. P.; Haertlein, M.; Moulin, M.; Gutsche, I.; Zaccai, G.; DiDonato, J.; Hazen, S. L. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 36605-19 (2009).
Experimental data and computational models:
|
a) Small angle neutron scattering intensities for the protein component of nascent HDL (12 % D2O, collected at the Institute Laue-Langevin, Grenoble, France). |
|
|
b) The solution low-resolution structure of the protein component of nascent HDL obtained by small angle neutron scattering with contrast variation (12 % D2O, ILL data). |
|
|
c) Small angle neutron scattering intensities for the lipid component of nascent HDL (42 % D2O, collected at the Institute Laue-Langevin, Grenoble, France). |
|
 |
d) The solution low-resolution structure of the lipid component of nascent HDL obtained by small angle neutron scattering with contrast variation (42 % D2O, ILL data). |
 |
e) The Double Super Helix model of nascent HDL. Available at www.rcsb.org (accession code 3K2S). |
3) Congruency between biophysical data from multiple platforms and molecular dynamics simulation of the double super helix model of nascent high-density lipoprotein
Gogonea, V.; Wu, Z.; Lee, X.; Pipich, V.; Li, X.-M., Ioffe, I. A.; DiDonato, J.; Hazen, S. L. Biochemistry, 49, 7323-43 (2010).
Experimental and computational models, and data calculated from simulation trajectory:
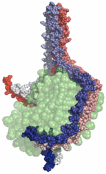
4) The low resolution structure of ApoA1 in spherical high density lipoprotein revealed by small angle neutron scattering
Wu, Z.; Gogonea, V.; Lee, X.; May, R.P.; Pipich, V.; Wagner, M.A.; Undurti, A.; Tallant, T. C.; Baleanu-Gogonea, C.; Charlton, F.; Ioffe, I. A.; DiDonato, J.A.; Rye, K.-A.; Hazen, S. L. J. Biol. Chem., 286, 12495-508 (2011).
Low resolution structures:
|
a) Small angle neutron scattering intensities for the protein component of spherical HDL (12 % D2O). |
|
 |
|
|
c) Small angle neutron scattering intensities for the lipid component of spherical HDL (42 % D2O). |
|
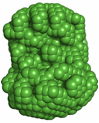 |
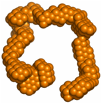
5) The low resolution structure of nascent high density lipoprotein reconstituted with DMPC with and without cholesterol reveals a mechanism for particle expansion
Gogonea, V.; Gerstenecker, G. S.; Wu, Z.; Lee, X.; Topbas, C.; Wagner, M. A.; Tallant, T. C.; Smith J. D.; Callow, P.; Pipich, V.; Malet, H.; Schoehn, G.; DiDonato, J. A.; Hazen, S. L. J. Lipid Res., in print.
Low resolution structures and computational model:
Our Team
Selected Publications
View publications for Stanley Hazen, MD, PhD
(Disclaimer: This search is powered by PubMed, a service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. PubMed is a third-party website with no affiliation with Cleveland Clinic.)
- Wang Z, Klipfell E, Bennett BJ, Koeth R, Levison BS, Dugar B, Feldstein AE, Britt EB, Fu X, Chung YM, Wu Y, Schauer P, Smith JD, Allayee H, Tang WHW, DiDonato JA, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature.(2011) 472(7341):57-63. PMCID: PMC3086762
- Tang WH, Wang Z, Levison BS, Koeth RA, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Hazen SL. Intestinal Microbial Metabolism of Phosphatidylcholine and Cardiovascular Risk. New England Journal of Medicine. (2013) 368(17):1575-84. PMCID: PMC3701945
- Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, Buffa J, Org E, Sheehy B, Li H, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Smith JD, DiDonato JA, Chen J, Li H, Wu G, Lewis JD, Warrier M, Brown, JM, Krauss RM, Tang WH, Bushman FD, Lusis AJ, and Hazen SL. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-Carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nature Medicine. (2013) 19(5): 576-85. PMCID: PMC36501111
- Huang Y, Didonato JA, Levison BS, Schmitt D, Li L, Wu Y, Buffa J, Kim T, Gerstenecker GS, Gu X, Kadiyala CS, Wang Z, Culley MK, Hazen JE, Didonato AJ, Fu X, Berisha SZ, Peng D, Nguyen TT, Liang S, Chuang CC, Cho L, Plow EF, Fox PL, Gogonea V, Tang WH, Parks JS, Fisher EA, Smith JD, Hazen SL. An abundant dysfunctional apolipoprotein A1 form in human atheroma. Nature Medicine. (2014) 20(2):193-203. PMCID: PMC3923163
- Gregory JC, Buffa JA, Org E, Wang Z, Levison BS, Zhu W, Wagner MA, Bennett BJ, Li L, DiDonato JA, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL. Transmission of Atherosclerosis Susceptibility with Gut Microbial Transplantation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. (2015) 290(9):5647-60 PMCID: PMC4342477
- Tang WHW, Wang Z, Kennedy DJ, Wu Y, Buffa J, Agatisa-Boyle B, Li XS, Levison BS, Hazen SL. The Gut Microbiota-Dependent Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) Pathway Contributes to both Development of Renal Insufficiency and Mortality Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease. Circulation Research. (2015) 116(3):448-55 PMCID: PMC4312512
Careers
Training at Lerner Research Institute
Our education and training programs offer hands-on experience at one of the nationʼs top hospitals. Travel, publish in high impact journals and collaborate with investigators to solve real-world biomedical research questions.
Learn MoreResearch News

The findings raise concerns about the safety of consuming sugar alcohols, especially for those at increased risk for cardiac disease.

Higher TMAO levels were also associated with a faster rate of declining kidney function in people with normal or impaired kidney function at baseline.

Study outlines genetic links between 4PY and vascular inflammation, indicates need for future research.

Inching closer to precision heart care medicine, Cleveland Clinic researchers develop an “atlas” of the human microbiome pathways linked to cardiac and mortality risks.

The additive’s clinical association with cardiovascular risk, coupled with increased clotting in preclinical models, showcases the need for further safety studies.

Two distinct gut microbial enzyme pathways could be targeted in therapeutic development.

New study finds elevated levels of the metabolite phenylacetylglutamine are associated with increased risk of heart failure.

Building on more than a decade of research from Dr. Stanley Hazen’s lab, researchers explored how elevated levels of trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) could serve as a warning sign for heart disease

Dr. Hazen identified the gbu gene cluster as a potential therapeutic target for diet-associated cardiovascular disease, and showed that dietary modifications may also help reduce risk.

Dr. Sharifi and collaborators identified choline, betaine and phenylacetylglutamine as nutrients and gut microbiome metabolites associated with increased risk for lethal prostate cancer, suggesting dietary interventions may help reduce disease risk.