Center for Immunotherapy & Precision Immuno-Oncology
About Immunotherapy
The Future of
Cancer Treatment
Impactful, Individualized, Innovative
To render a precise anti-tumor immune response, multi-faceted research on immunotherapy treatment strategies often involves one or more immunotherapeutics coupled with chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery.
Harnessing the Immune System
While traditional methods for treating cancer, including chemotherapy and radiation, are often effective at killing cancer cells, they can also kill healthy cells. Cancer researchers are developing new effective therapies using a variety of approaches combined with immunotherapy to target cancer while limiting treatment-related toxicities. Immunotherapies, which harness a patient's immune system to fight cancer, have been shown to enhance survival in many cancers. Immunotherapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, adoptive cell therapy, cancer vaccines, and immunomodulators are revolutionizing treatment for a growing number of human cancers.
Learn More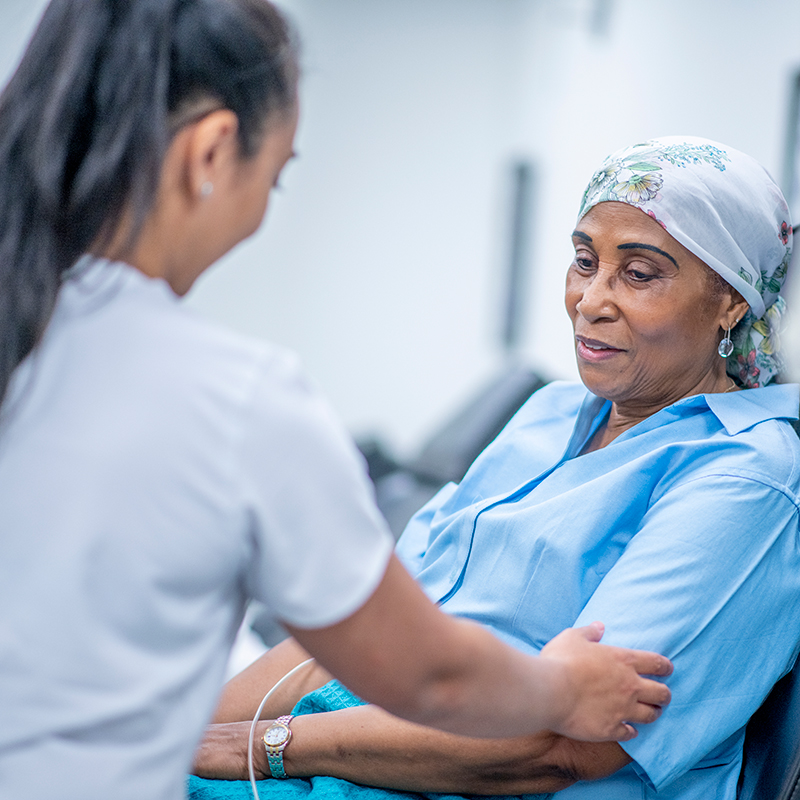
Research by Immunotherapy Treatment Type
In cell therapy, immune cells such as T lymphocytes or NK cells are isolated from a patient's own immune system, genetically engineered, expanded in the laboratory, and subsequently infused back into the patient to target and eliminate cancer cells. Types of cell therapy include CAR T therapy and adoptive cell therapy. CITI has active programs that involve the development of new CAR T cells and the testing of new cell therapies in clinical trials. We also work closely with the Bone Marrow Transplant and Cell Therapy Service in the Taussig Cancer Center. Select highlights are as follows:
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are antibodies that can target tumors and deliver drugs. They are used to treat cancers and have been shown to be effective in many settings. These include treatments for breast cancer, lung cancer, and many other types of malignancies. Targeted antibodies can inhibit pathways needed for cancer growth. Select highlights are as follows:

Cancer vaccines stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells. Preventative cancer vaccines are intended to thwart the onset of cancer and therapeutic vaccines are designed to treat cancer treatment after diagnosis. Select highlights are as follows:
Immune system modulators include cytokines, bacillus calmette guerin (BCG), and immunomodulatory drugs. Cytokines are sometimes used to either treat cancer or reduce side effects from cancer treatment. A highlighted example is a multi-center trial (NCT05665062) on Autologous CD19 CAR-T Cell Therapy + IL-2 in Subjects with CD19+ Hematologic Malignancies.
Antibodies against immunoreactive molecules can be used to stimulate anti-tumor immunity. These antibodies include immune checkpoint inhibitors, which have revolutionized the treatment of many cancer types. Antibodies against PD-1, PD-L1, and others are immune checkpoint inhibitors that have increased survival in cancer patients. Select highlights are as follows:

If you'd like to learn more about treatment options, referrals, or making appointments, please call the Cancer Answer line at 866.223.8100. Designated caregivers and advanced practice nurses can answer any questions and refer you to appropriate personnel. The Cancer Answer staff also works closely with CCF's new Novel Therapeutics Clinic (NTC), a consult clinic for solid tumor patients who may benefit from early phase clinical trials. Visit Cleveland Clinic Cancer Center for even more information.
Partners in Research
In the Center for Immunotherapy & Precision Immuno-Oncology, scientists are studying the interplay between the immune system and tumor microenvironment. Our institution includes efforts in basic sciences, translational and clinical trials, technology development, and precision oncology services. We are partners in industry-sponsored trials with clinicians and researchers across the Cleveland Clinic enterprise and the Case Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Cleveland Clinic
Case Comprehensive Cancer Center
National Center for Regenerative Medicine